Spark Dynamic Allocation
In Spark, the fundamental resource unit is the executor, which is similar to containers in YARN. When running Spark on YARN, you can specify the number of executors using the num-executors parameter. Additionally, executor-memory and executor-cores parameters limit the memory and virtual CPU cores allocated to each executor.
Consider a Kylin instance as an example. When using a fixed resource allocation strategy with num-executor set to 3, each Kylin instance will occupy 4 YARN containers (1 for the application master and 3 for executors) until the user logs out. In contrast, Dynamic Resource Allocation enables Spark to dynamically adjust the number of executors based on the Kylin query engine workload, resulting in significant resource savings.
For more information on Spark Dynamic Allocation, please refer to the official Spark documentation: http://spark.apache.org/docs/2.4.1/job-scheduling.html#dynamic-resource-allocation
Overview
Configuring Spark Dynamic Allocation involves two key components:
- Resource Management: This varies depending on the cluster's resource manager, which can be YARN, Mesos, or Standalone.
- spark-defaults.conf: This configuration file is environment-agnostic and applies universally.
Config ResourceManager
-
For CDH
Log into Cloudera Manager, choose YARN configuration and find NodeManager Advanced Configuration Snippet(Safety Valve) for
yarn-site.xml, config as following:<property>
<name>yarn.nodemanager.aux-services</name>
<value>mapreduce_shuffle,spark_shuffle</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>yarn.nodemanager.aux-services.spark_shuffle.class</name>
<value>org.apache.spark.network.yarn.YarnShuffleService</value>
</property>Copy the
$KYLIN_HOME/spark/yarn/spark-<version>-yarn-shuffle.jarand put it under path/opt/lib/kylin/of Hadoop node. Find NodeManager Environment Advanced Configuration Snippet (Safety Valve) in Cloudera Manager, Config:YARN_USER_CLASSPATH=/opt/lib/kylin/*Then
yarn-shuffle.jarwill be added into the Node Manager's startup classpath. To apply the changes, save the configuration, restart the Node Manager, and then deploy the client configuration in Cloudera Manager. Finally, restart all services to ensure the updates take effect. -
For HDP
Log into Ambari management page, navigate to Yarn -> Configs -> Advanced, use the filter to find the following configurations and update them as needed:
yarn.nodemanager.aux-services.spark_shuffle.class=org.apache.spark.network.yarn.YarnShuffleServiceTo apply the changes, save the configuration, and restart all services to ensure the updates take effect.
How to Enable
To enable the Spark Dynamic Allocation, we will need to add some configuration items in Spark config files. Since we can override spark configuraion in kylin.properties, we will add following configuration items in it:
kylin.storage.columnar.spark-conf.spark.dynamicAllocation.enabled=true
kylin.storage.columnar.spark-conf.spark.dynamicAllocation.maxExecutors=5
kylin.storage.columnar.spark-conf.spark.dynamicAllocation.minExecutors=1
kylin.storage.columnar.spark-conf.spark.shuffle.service.enabled=true
kylin.storage.columnar.spark-conf.spark.dynamicAllocation.initialExecutors=3
More configurations please refer to: http://spark.apache.org/docs/latest/configuration.html#dynamic-allocation
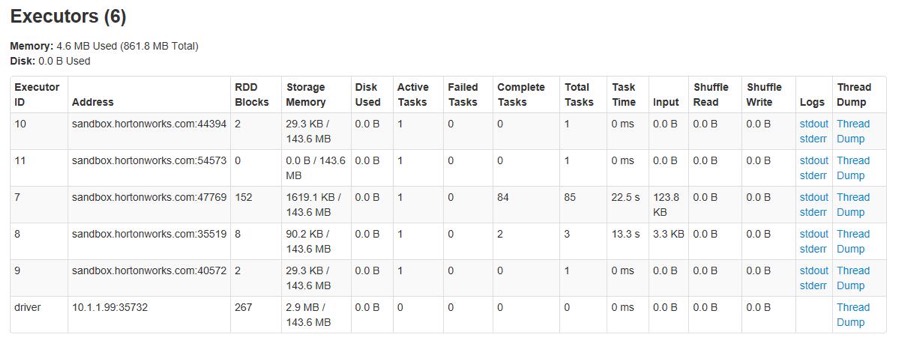
How to Verification
After completing the configurations, start the Kylin service and navigate to the Spark Executor page to monitor the current executor numbers. Observe how the executor count adjusts dynamically based on the defined settings.
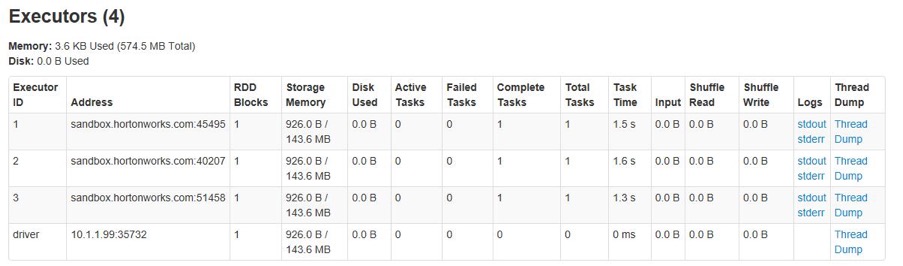
The executors will keep idle, so they will be reduced after a while until reaching the minimum number in configuration item.
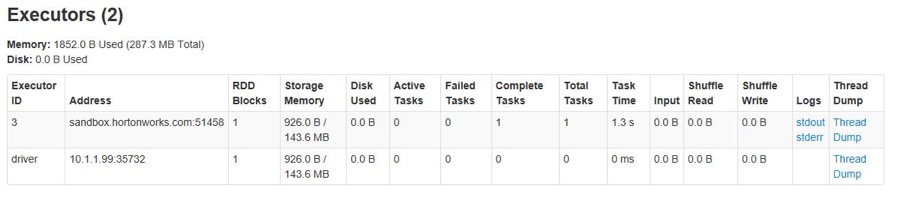
Submit multi-thread queries to Kylin via Restful API. The executors will be increase but never exceed the maximum number in configuration item.