The future of Apache Kylin:More powerful and easy-to-use OLAP
01 Apache Kylin Today
Currently, the latest release of Apache Kylin is 4.0.1. Apache Kylin 4.0 is a major version update after Kylin 3.x (HBase Storage). Kylin 4.0 uses Parquet to replace HBase as storage engine, so as to improve file scanning performance. At the same time, Kylin 4.0 reimplements the spark based build engine and query engine, making it possible to separate computing and storage, and better adapt to the technology trend of cloud native.
Kylin 4.0 comprehensively updated the build and query engine, realized the deployment mode without Hadoop dependency, decrease the complexity of deployment. In addition, combined with the feedback of Kylin users and the trend of OLAP technology, Kylin community found that there are still some weaknesses and deficiencies in today’s Apache Kylin, such as the ability of business semantic layer needs to be strengthened and the modification of model/cube is not flexible. With these, we thinking a few things to do::
- Multi-dimensional query ability friendly to non-technical personnel. Multi-dimensional model is the key to distinguish Kylin from general OLAP engine. The feature is that the model concept based on dimension and measurement is more friendly to non-technical personnel and closer to the goal of “everyone is a data analyst”. The multi-dimensional query capability that non-technical personnel can use should be the new focus of Kylin technology.
- Native Engine. The query engine of Kylin still has much room for improvement in vector acceleration and cpu instruction level optimization. The Spark community Kylin relies on also has a strong demand for native engine. It is optimistic that native engine can improve the performance of Kylin by at least three times, which is worthy of investment.
- More cloud native capabilities. Kylin 4.0 has only completed the initial cloud deployment and realized the features of rapid deployment and dynamic resource scaling on the cloud, but there are still many cloud native capabilities to be developed.
More explanations are following.
02 KYLIN AS A MULTI-DIMENSIONAL DATABASE
The core of Kylin is a multi-dimensional database, which is a special OLAP engine. Although Kylin has always had the ability of relational database since its birth, and it is often compared with other relational OLAP engines, what really makes Kylin different is multi-dimensional model and multi-dimensional database ability. Considering the essence of Kylin and its wide range of business uses in the future (not only technical uses), we will clearly position Kylin as a multi-dimensional database. We also hope that through multi-dimensional model and precomputation technology, Apache Kylin can make non-technical people understand and afford big data, and finally realize data democratization.
THE SEMANTIC LAYER
The key difference between multi-dimensional database and relational database is business expression ability. Although SQL has strong expression ability and is the basic skill of data analysts, SQL and relational database are still too difficult for non-technical personnel if we aim at “everyone is a data analyst”. From the perspective of non-technical personnel, the data lake and data warehouse are like a dark room. They know that there is a lot of data, but they can’t see clearly, understand and use this data because they don’t understand database theory and SQL.
How to make the Data Lake (and data warehouse) clear to non-technical personnel? This requires introducing a more friendly data model for non-technical personnel —— multi-dimensional data model. While the relational model describes the technical form of data, the multi-dimensional model describes the business form of data. In multi-dimensional database, measurement corresponds to business indicators that everyone understands, and dimension is the perspective of comparing and observing these business indicators. Compare KPI with last month and compare performance between parallel business units, which are concepts understood by every non-technical personnel. By mapping the relational model to the multi-dimensional model, the essence is to enhance the business semantics on the technical data, form a business semantic layer, and help non-technical personnel understand, explore and use the data.
In order to enhance Kylin’s ability as the semantic layer of multi-dimensional database, supporting multi-dimensional query language is the key content of Kylin roadmap, such as MDX and DAX. MDX can transform the data model in Kylin into a business friendly language, endow data with business value, and facilitate Kylin’s multi-dimensional analysis with BI tools such as Excel and Tableau.
PRECOMPUTATION AND MODEL FLEXIBILITY
It is kylin’s unchanging mission to continue to reduce the cost of a single query through precomputation technology so that ordinary people can afford big data. If the multi-dimensional model solves the problem that non-technical personnel can understand data, then precomputation can solve the problem that ordinary people can afford data. Both are necessary conditions for data democratization. Through one calculation and multiple use, the data cost can be shared by multiple users to achieve the scale effect that the more users, the cheaper. Precalculation is Kylin’s traditional strength, but it lacks some flexibility in the change of precalculation model. In order to strengthen the ability to change models flexibly of Kylin and bring more optimization room, Kylin community expects to propose a new metadata format in Kylin in the future to make precalculation more flexible, be able to cope with that table format or business requirements may change at any time.
SUMMARY
To sum up, we will make it clear that Kylin’s technical position is a multi-dimensional database. Through multi-dimensional model and precomputation technology, ordinary people can understand and afford big data, and finally realize the vision of data democratization. Meanwhile, for today’s users who use Kylin as the SQL acceleration layer, Kylin will continue to maintain a complete SQL interface to ensure that the precomputation technology can be used by both relational model and multi-dimensional model.
In the figure below, we can clearly see the direction of Kylin’s attention in the future. The newly added and modified parts are roughly marked in blue and orange.
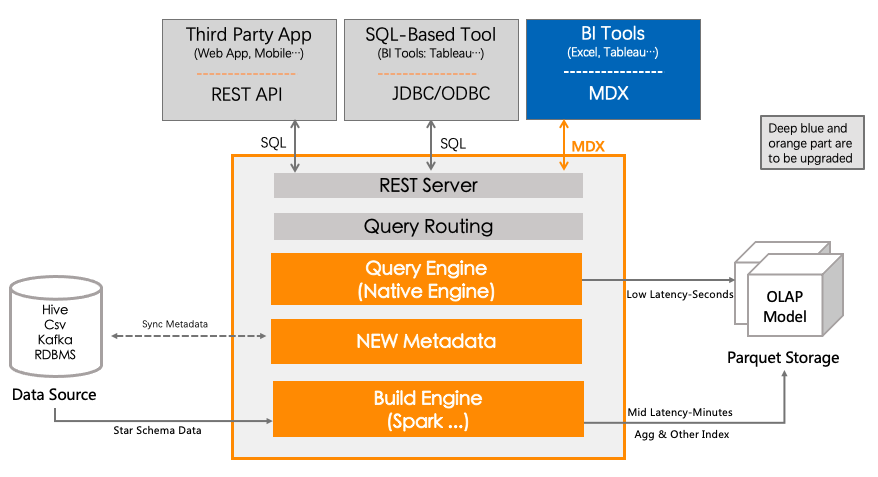
03 THE FUTURE PLAN
Based on Kylin’s positioning as a multi-dimensional database, combined with the existing capabilities of Kylin that need to be strengthened, and in order to support the long-awaited features of users such as schema change, we plan to introduce a new metadata format of DataModel into Kylin : no longer expose Cube to users, but simplify the metadata dependency to ‘Model -> Table’.
As metadata is the basis and contract for the subsequent collaborative development of Kylin, the design and development of the new metadata format will be the focus of Kylin community’s work at present and in the next few months. The metadata design and discussion proposal will be released later. You are welcome to participate in the discussion. Not surprisingly, the new metadata format will meet you this year.
In addition to metadata format upgrading, the build and query engine which support metadata upgrade, semantic layer capability (MDX), better integration with BI tools and native engine are also the key work that Kylin community has been actively promoting. More like-minded users and developers are welcome to participate in development and promote Kylin community development jointly.
** Further Reading **
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Data_model
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Semantic_layer
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Multidimensional_analysis
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/MultiDimensional_eXpressions
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/XML_for_Analysis
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/SIMD
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cloud_native_computing
- https://blogs.gartner.com/carlie-idoine/2018/05/13/citizen-data-scientists-and-why-they-matter/
