Kylin v1.6 releases the scalable streaming cubing function, it leverages Hadoop to consume the data from Kafka to build the cube, you can check this blog for the high level design. This doc is a step by step tutorial, illustrating how to create and build a sample cube;
If you prefer to ingest kafka event immediately other than micro batch way and get query result in very low-latency(less than 1 seconds), you may consider using the new feature Real-time OLAP which introduced in Kylin v3.0.
Preparation
To finish this tutorial, you need a Hadoop environment which has kylin v1.6.0 or above installed; Since kylin v2.5.0, it needs a Kafka v1.0.0 or above.
In this tutorial, we will use Hortonworks HDP 2.2.4 Sandbox VM + Kafka v1.0.2(Scala 2.11) as the environment.
Install Kafka and Kylin
Don’t use HDP 2.2.4’s build-in Kafka as it is too old, stop it first if it is running. Please download Kafka 1.0 binary package from Kafka project page, and then uncompress it under a folder like /usr/local/.
tar -zxvf
cd /usr/local/kafka_2.11-1.0.2
bin/kafka-server-start.sh config/server.properties &Download the Kylin, expand the tar ball in /usr/local/ folder.
Create sample Kafka topic and populate data
Create a sample topic “kylin_streaming_topic”, with 3 partitions:
bin/kafka-topics.sh --create --zookeeper localhost:2181 --replication-factor 1 --partitions 3 --topic kylin_streaming_topic
Created topic "kylin_streaming_topic".Put sample data to this topic; Kylin has an utility class which can do this;
export KAFKA_HOME=/usr/local/kafka_2.11-1.0.2
export KYLIN_HOME=/usr/local/apache-kylin-2.6.0-bin
cd $KYLIN_HOME
./bin/kylin.sh org.apache.kylin.source.kafka.util.KafkaSampleProducer --topic kylin_streaming_topic --broker localhost:9092This tool will send 100 records to Kafka every second (there is a bug in v2.6.0 on this, please check KYLIN-3793). Please keep it running during this tutorial. You can check the sample message with kafka-console-consumer.sh now:
cd $KAFKA_HOME
bin/kafka-console-consumer.sh --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --topic kylin_streaming_topic --from-beginning
{"amount":63.50375137330458,"category":"TOY","order_time":1477415932581,"device":"Other","qty":4,"user":{"id":"bf249f36-f593-4307-b156-240b3094a1c3","age":21,"gender":"Male"},"currency":"USD","country":"CHINA"}
{"amount":22.806058795736583,"category":"ELECTRONIC","order_time":1477415932591,"device":"Andriod","qty":1,"user":{"id":"00283efe-027e-4ec1-bbed-c2bbda873f1d","age":27,"gender":"Female"},"currency":"USD","country":"INDIA"}Define a table from streaming
Start Kylin server with “$KYLIN_HOME/bin/kylin.sh start”, login Kylin Web GUI at http://sandbox:7070/kylin/, select an existing project or create a new project; Click “Model” -> “Data Source”, then click the icon “Add Streaming Table”; (Attention: the option Add Streaming Table V2 is for the Realtime OLAP feature which introduced in Kylin v3.0, don’t mix them).
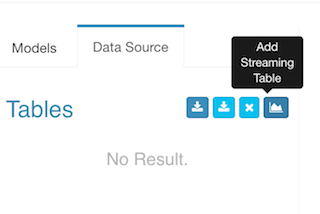
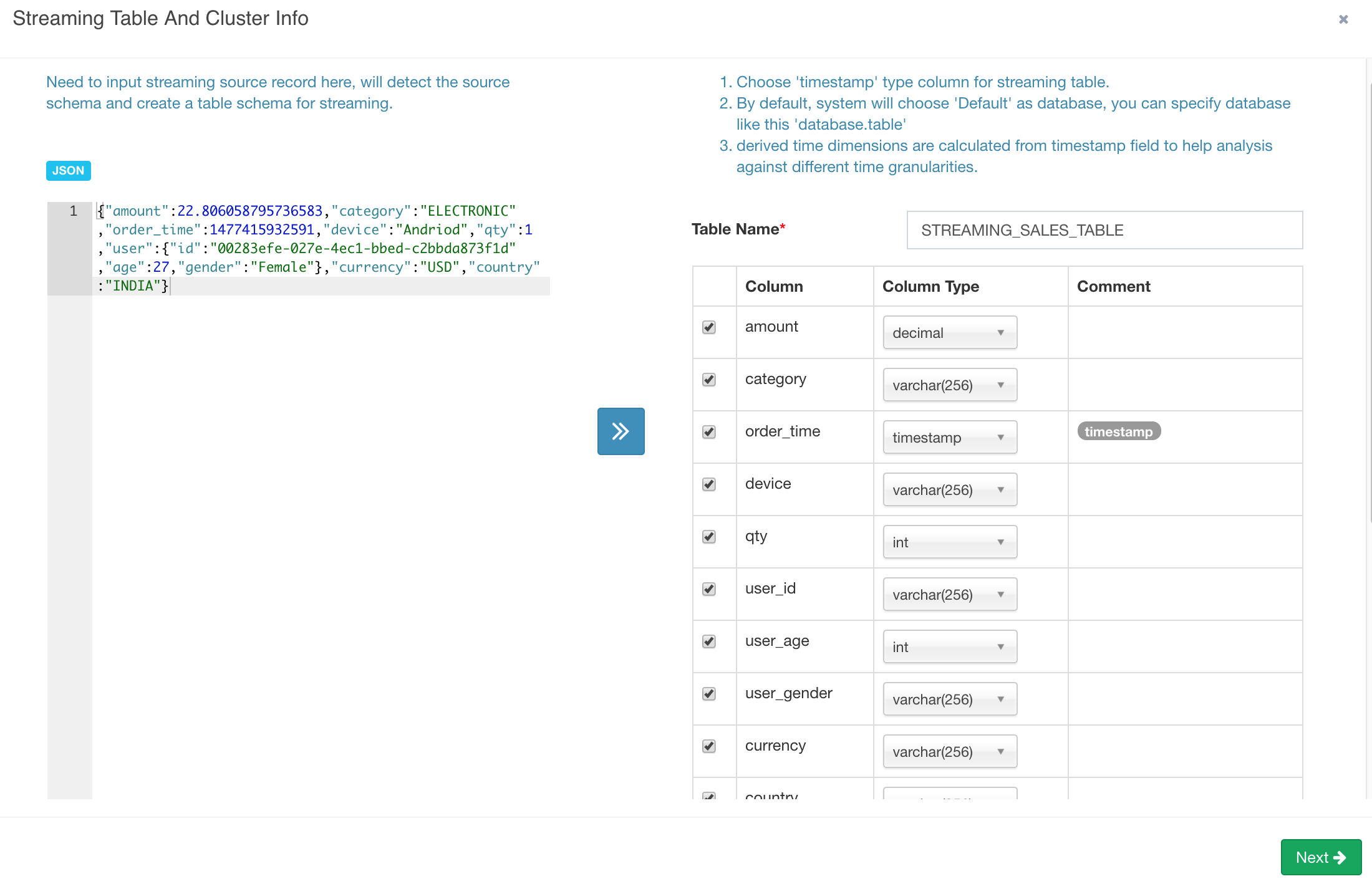
In the pop-up dialogue, enter a sample record which you got from the kafka-console-consumer, click the “»” button, Kylin parses the JSON message and lists all the properties;
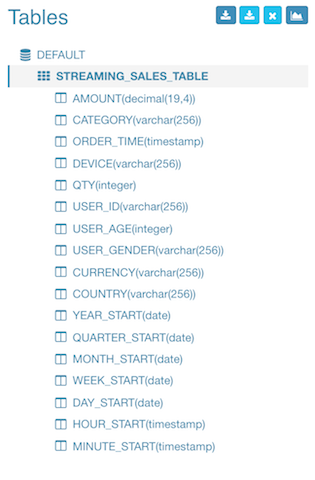
You need give a logic table name for this streaming data source; The name will be used for SQL query later; here enter “STREAMING_SALES_TABLE” as an example in the “Table Name” field.
You need select a timestamp field which will be used to identify the time of a message; Kylin can derive other time values like “year_start”, “quarter_start” from this time column, which can give your more flexibility on building and querying the cube. Here check “order_time”. You can deselect those properties which are not needed for cube. Here let’s keep all fields.
Notice that Kylin supports structured (or say “embedded”) message from v1.6, it will convert them into a flat table structure. By default use “_” as the separator of the structed properties.
Click “Next”. On this page, provide the Kafka cluster information; Enter “kylin_streaming_topic” as “Topic” name; The cluster has 1 broker, whose host name is “sandbox”, port is “9092”, click “Save”.
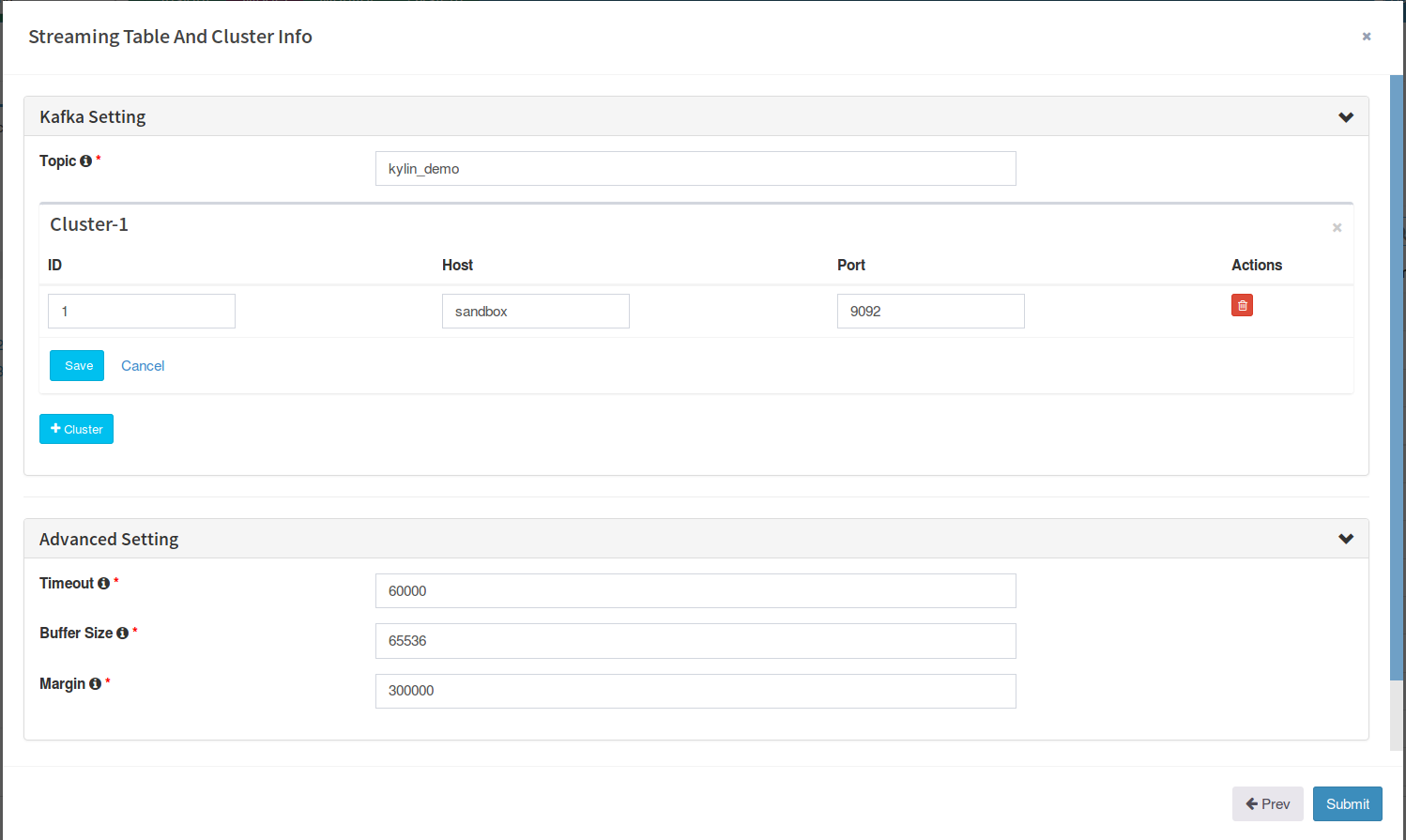
In “Advanced setting” section, the “timeout” and “buffer size” are the configurations for connecting with Kafka, keep them.
In “Parser Setting”, by default Kylin assumes your message is JSON format, and each record’s timestamp column (specified by “tsColName”) is a bigint (epoch time) value; in this case, you just need set the “tsColumn” to “order_time”;
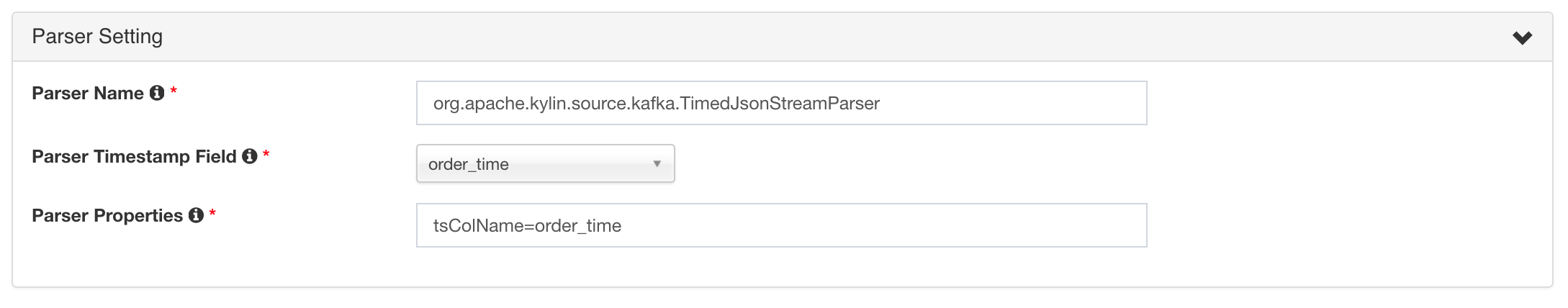
In real case if the timestamp value is a string valued timestamp like “Jul 20, 2016 9:59:17 AM”, you need specify the parser class with “tsParser” and the time pattern with “tsPattern” like this:
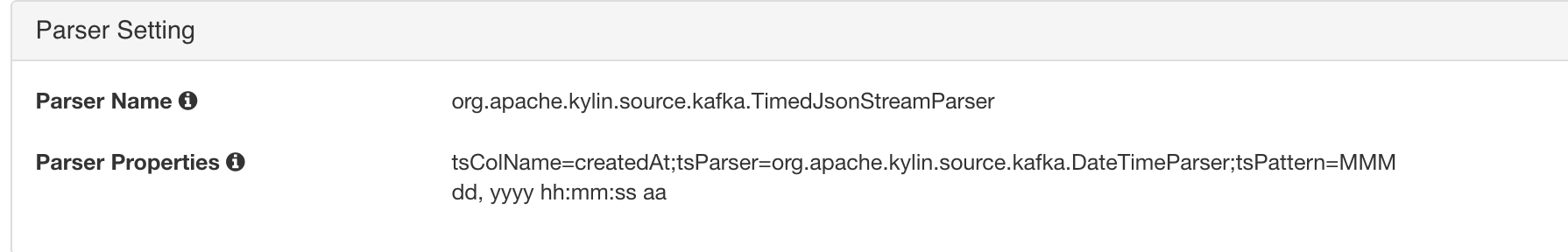
Click “Submit” to save the configurations. Now a “Streaming” table is created.
Define data model
With the table defined in previous step, now we can create the data model. The step is almost the same as you create a normal data model, but it has two requirement:
- Before v2.4.0, Streaming Cube doesn’t support join with lookup tables; When define the data model, only select fact table, no lookup table;
- If with v2.4.0 or above, you can add lookup tables to the data model. All lookup tables need to be Hive tables;
- Streaming Cube must be partitioned; If you’re going to build the Cube incrementally at minutes level, select “MINUTE_START” as the cube’s partition date column. If at hours level, select “HOUR_START”.
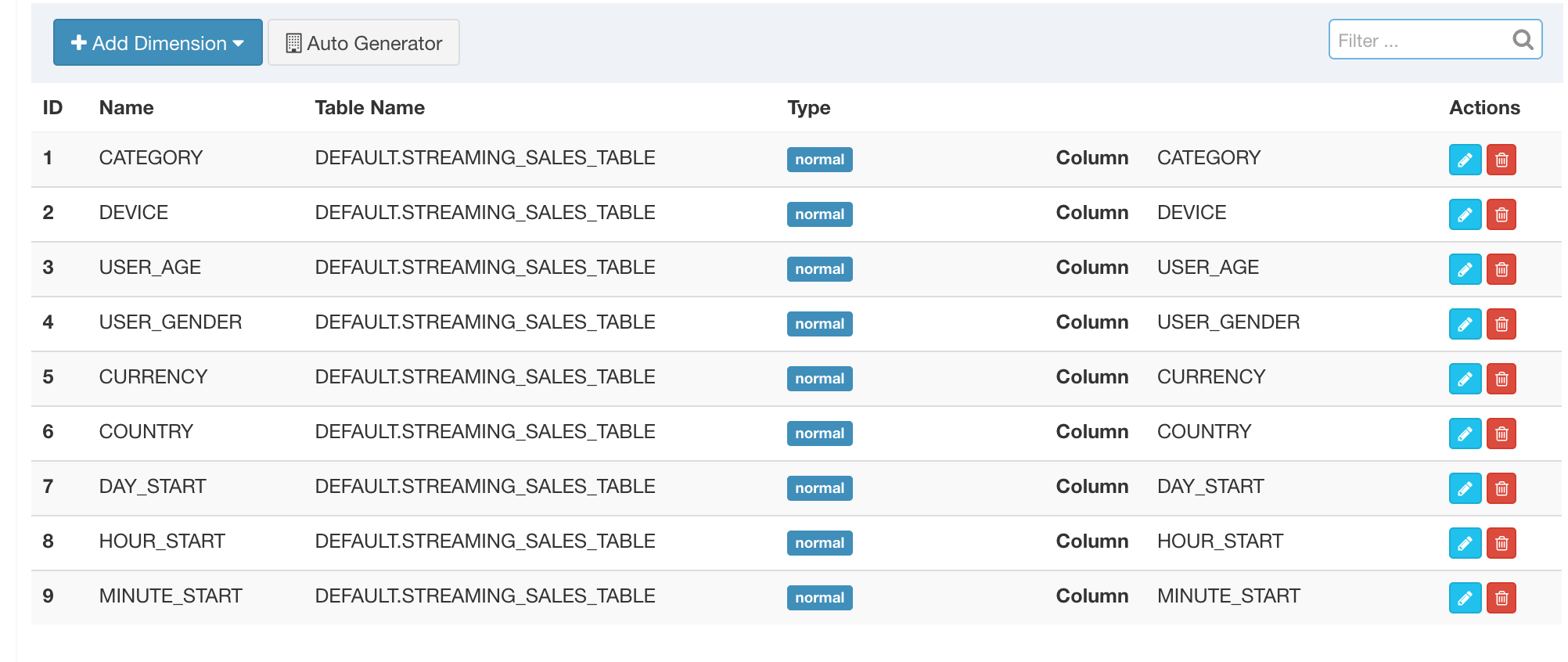
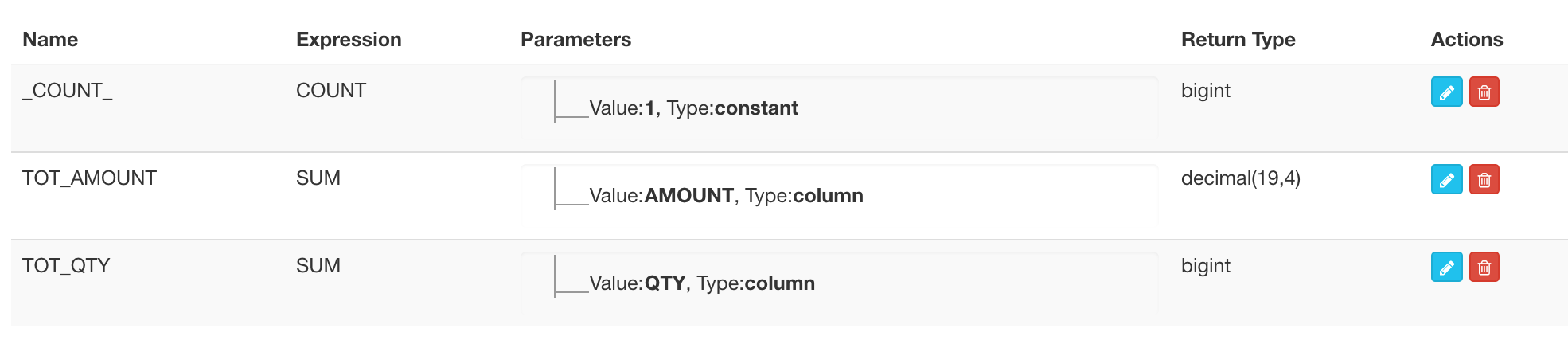
Here we pick 13 dimension and 2 measure columns:
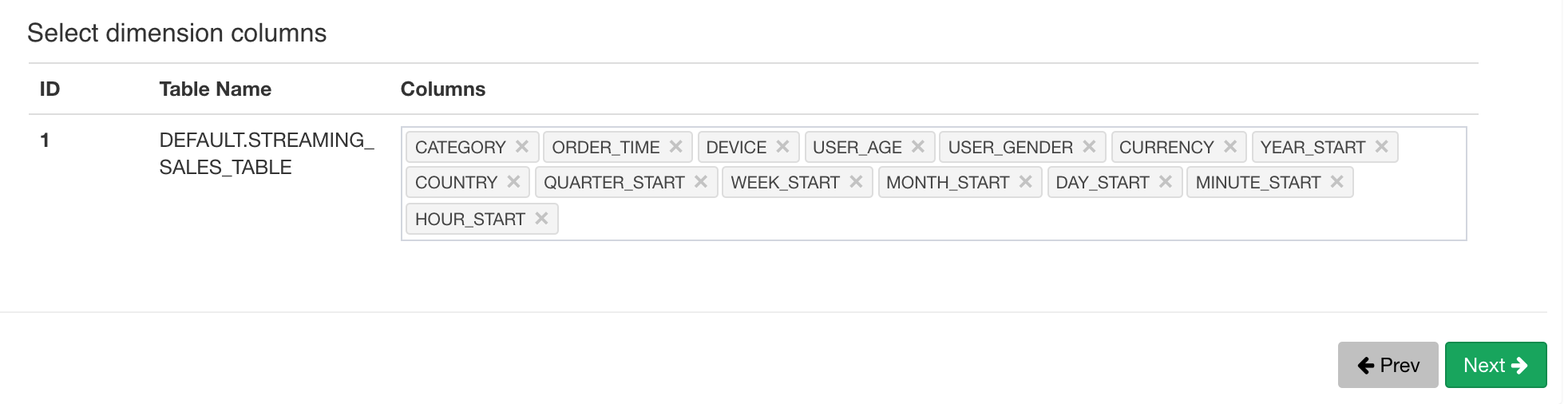
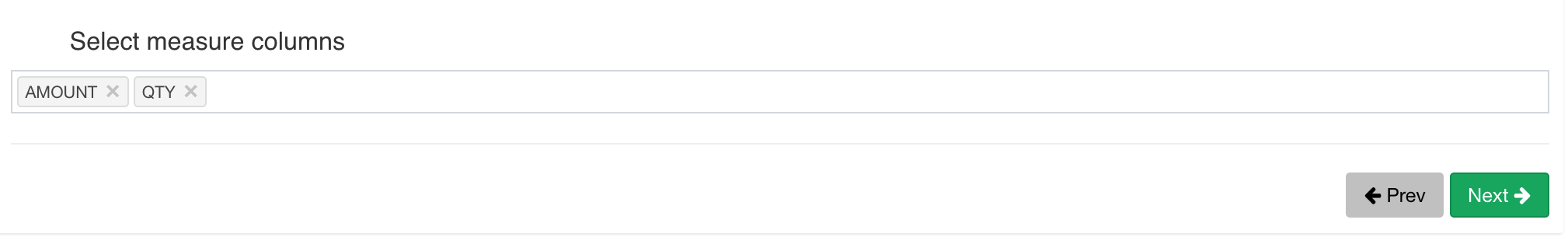
Save the data model.
Create Cube
The streaming Cube is almost the same as a normal cube. a couple of points need get your attention:
- The partition time column should be a dimension of the Cube. In Streaming OLAP the time is always a query condition, and Kylin will leverage this to narrow down the scanned partitions.
- Don’t use “order_time” as dimension as that is pretty fine-grained; suggest to use “minute_start”, “hour_start” or other, depends on how you will inspect the data.
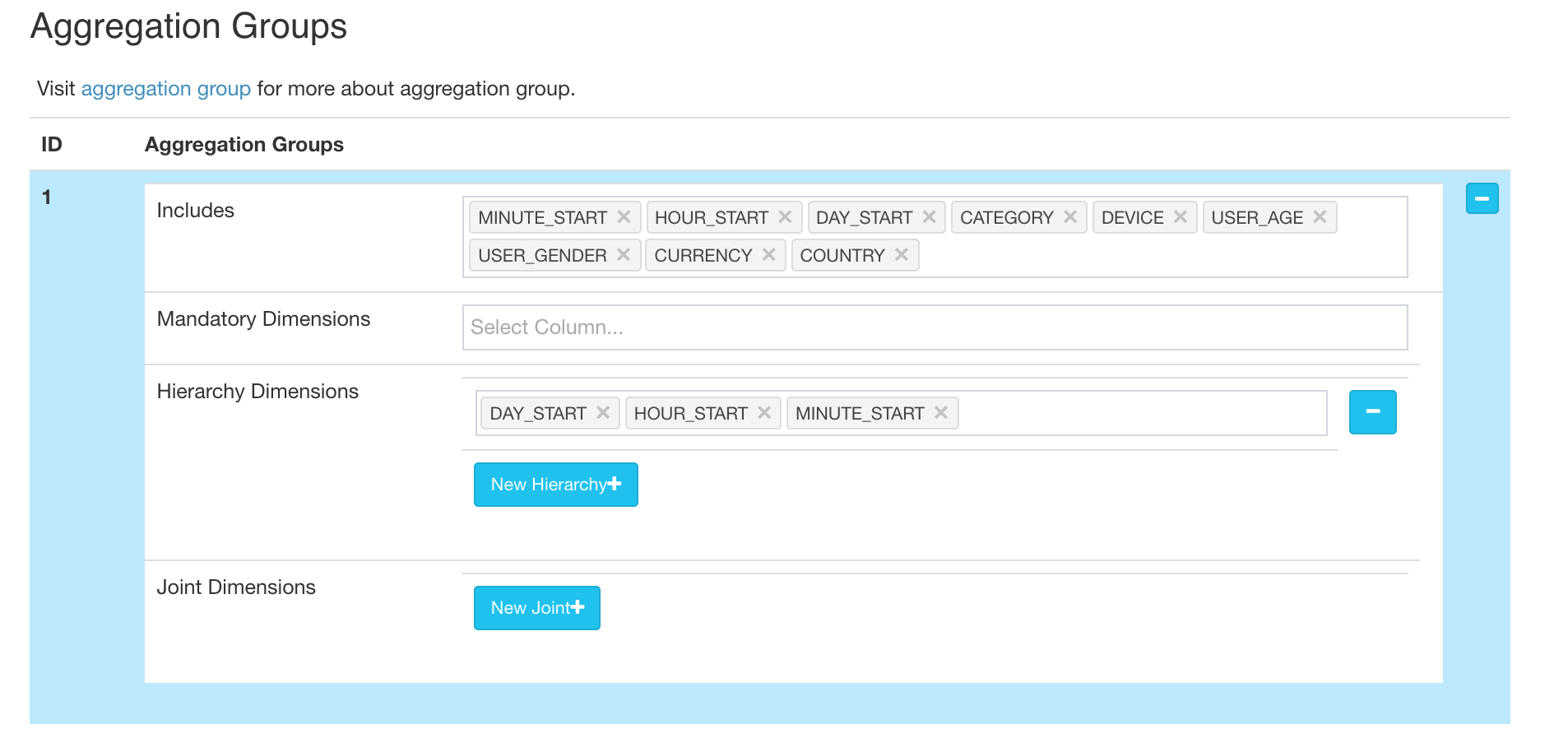
- Define “year_start”, “quarter_start”, “month_start”, “day_start”, “hour_start”, “minute_start” as a hierarchy to reduce the combinations to calculate.
- In the “refresh setting” step, create more merge ranges, like 0.5 hour, 4 hours, 1 day, and then 7 days; This will help to control the cube segment number.
-
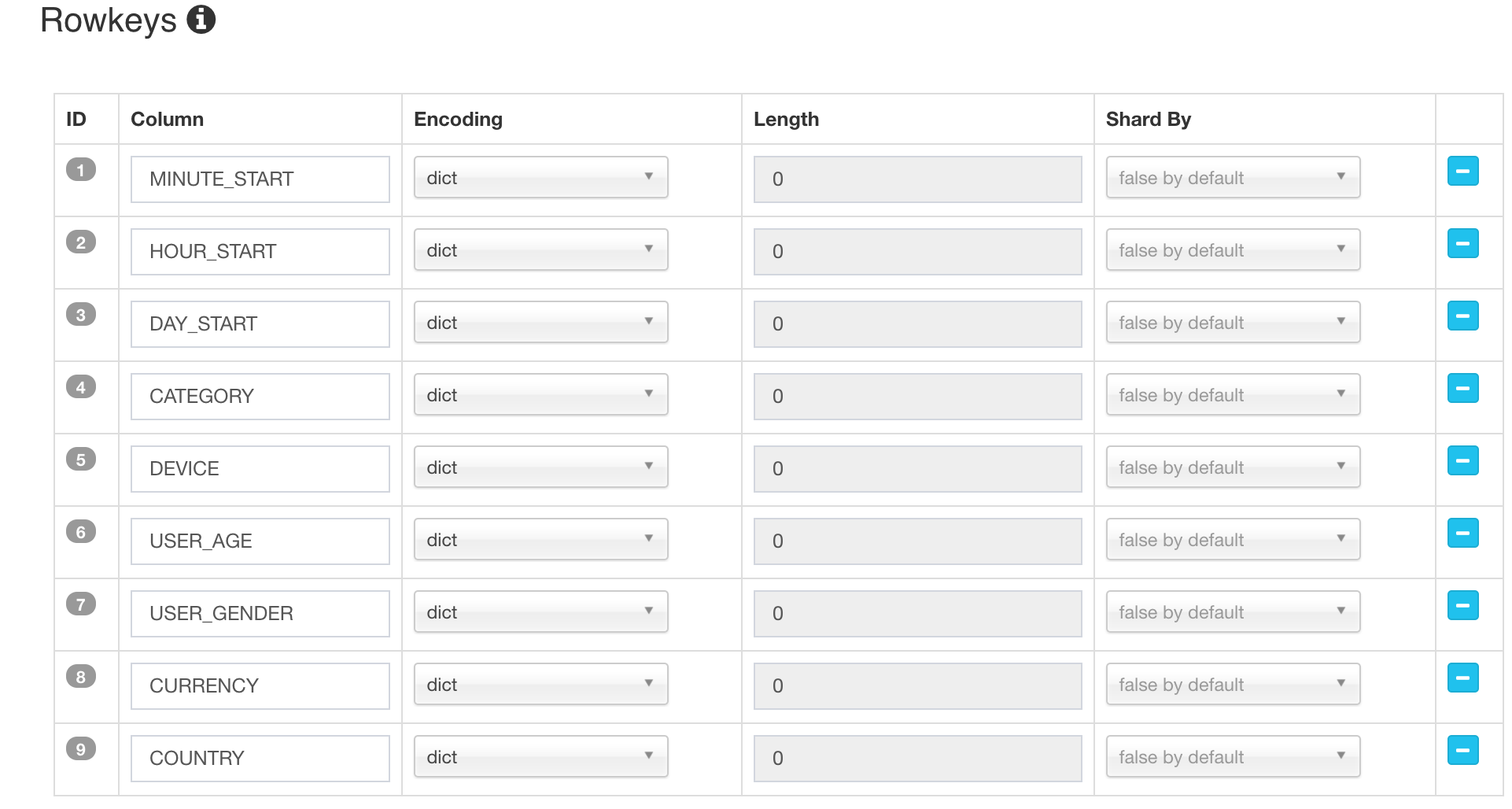
In the “rowkeys” section, drag&drop the “minute_start” to the head position, as for streaming queries, the time condition is always appeared; putting it to head will help to narrow down the scan range.
Save the cube.
Run a build
You can trigger the build from web GUI, by clicking “Actions” -> “Build”, or sending a request to Kylin RESTful API with ‘curl’ command:
curl -X PUT --user ADMIN:KYLIN -H "Content-Type: application/json;charset=utf-8" -d '{ "sourceOffsetStart": 0, "sourceOffsetEnd": 9223372036854775807, "buildType": "BUILD"}' http://localhost:7070/kylin/api/cubes/{your_cube_name}/build2Please note the API endpoint is different from a normal cube (this URL end with “build2”).
Here 0 means from the last position, and 9223372036854775807 (Long.MAX_VALUE) means to the end position on Kafka topic. If it is the first time to build (no previous segment), Kylin will seek to beginning of the topics as the start position.
In the “Monitor” page, a new job is generated; Wait it 100% finished.
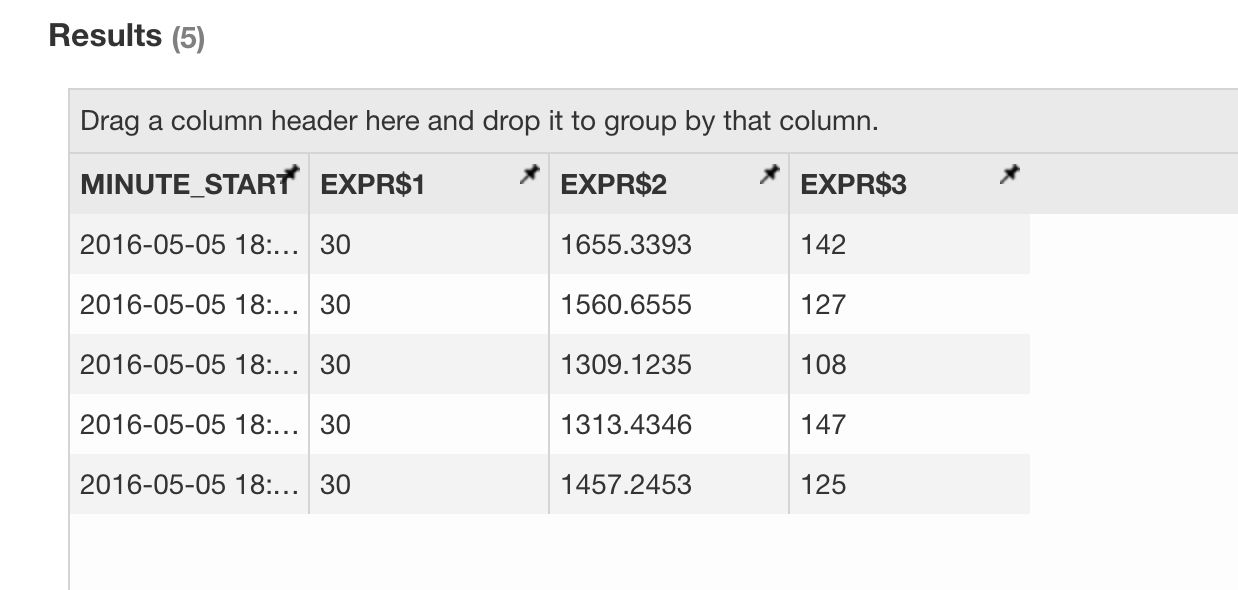
Click the “Insight” tab, compose a SQL to run, e.g:
select minute_start, count(*), sum(amount), sum(qty) from streaming_sales_table group by minute_start order by minute_startThe result looks like below.
Automate the build
Once the first build and query got successfully, you can schedule incremental builds at a certain frequency. Kylin will record the offsets of each build; when receive a build request, it will start from the last end position, and then seek the latest offsets from Kafka. With the REST API you can trigger it with any scheduler tools like Linux cron:
crontab -e
*/5 * * * * curl -X PUT --user ADMIN:KYLIN -H "Content-Type: application/json;charset=utf-8" -d '{ "sourceOffsetStart": 0, "sourceOffsetEnd": 9223372036854775807, "buildType": "BUILD"}' http://localhost:7070/kylin/api/cubes/{your_cube_name}/build2Now you can site down and watch the cube be automatically built from streaming. And when the cube segments accumulate to bigger time range, Kylin will automatically merge them into a bigger segment.
Trouble shootings
- You may encounter the following error when run “kylin.sh”:
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError: org/apache/kafka/clients/producer/Producer
at java.lang.Class.getDeclaredMethods0(Native Method)
at java.lang.Class.privateGetDeclaredMethods(Class.java:2615)
at java.lang.Class.getMethod0(Class.java:2856)
at java.lang.Class.getMethod(Class.java:1668)
at sun.launcher.LauncherHelper.getMainMethod(LauncherHelper.java:494)
at sun.launcher.LauncherHelper.checkAndLoadMain(LauncherHelper.java:486)
Caused by: java.lang.ClassNotFoundException: org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.Producer
at java.net.URLClassLoader$1.run(URLClassLoader.java:366)
at java.net.URLClassLoader$1.run(URLClassLoader.java:355)
at java.security.AccessController.doPrivileged(Native Method)
at java.net.URLClassLoader.findClass(URLClassLoader.java:354)
at java.lang.ClassLoader.loadClass(ClassLoader.java:425)
at sun.misc.Launcher$AppClassLoader.loadClass(Launcher.java:308)
at java.lang.ClassLoader.loadClass(ClassLoader.java:358)
... 6 moreThe reason is Kylin wasn’t able to find the proper Kafka client jars; Make sure you have properly set “KAFKA_HOME” environment variable.
- Get “killed by admin” error in the “Build Cube” step
Within a Sandbox VM, YARN may not allocate the requested memory resource to MR job as the “inmem” cubing algorithm requests more memory. You can bypass this by requesting less memory: edit “conf/kylin_job_conf_inmem.xml”, change the following two parameters like this:
<property>
<name>mapreduce.map.memory.mb</name>
<value>1072</value>
<description></description>
</property>
<property>
<name>mapreduce.map.java.opts</name>
<value>-Xmx800m</value>
<description></description>
</property>- If there already be bunch of history messages in Kafka and you don’t want to build from the very beginning, you can trigger a call to set the current end position as the start for the cube:
curl -X PUT --user ADMIN:KYLIN -H "Content-Type: application/json;charset=utf-8" -d '{ "sourceOffsetStart": 0, "sourceOffsetEnd": 9223372036854775807, "buildType": "BUILD"}' http://localhost:7070/kylin/api/cubes/{your_cube_name}/init_start_offsets- If some build job got error and you discard it, there will be a hole (or say gap) left in the Cube. Since each time Kylin will build from last position, you couldn’t expect the hole be filled by normal builds. Kylin provides API to check and fill the holes
Check holes:
curl -X GET --user ADMIN:KYLIN -H "Content-Type: application/json;charset=utf-8" http://localhost:7070/kylin/api/cubes/{your_cube_name}/holesIf the result is an empty arrary, means there is no hole; Otherwise, trigger Kylin to fill them:
curl -X PUT --user ADMIN:KYLIN -H "Content-Type: application/json;charset=utf-8" http://localhost:7070/kylin/api/cubes/{your_cube_name}/holes