Kylin instances are stateless services, and runtime state information is stored in the HBase metastore. For load balancing purposes, you can enable multiple Kylin instances that share a metastore, so that each node shares query pressure and backs up each other, improving service availability. The following figure depicts a typical scenario for Kylin cluster mode deployment:
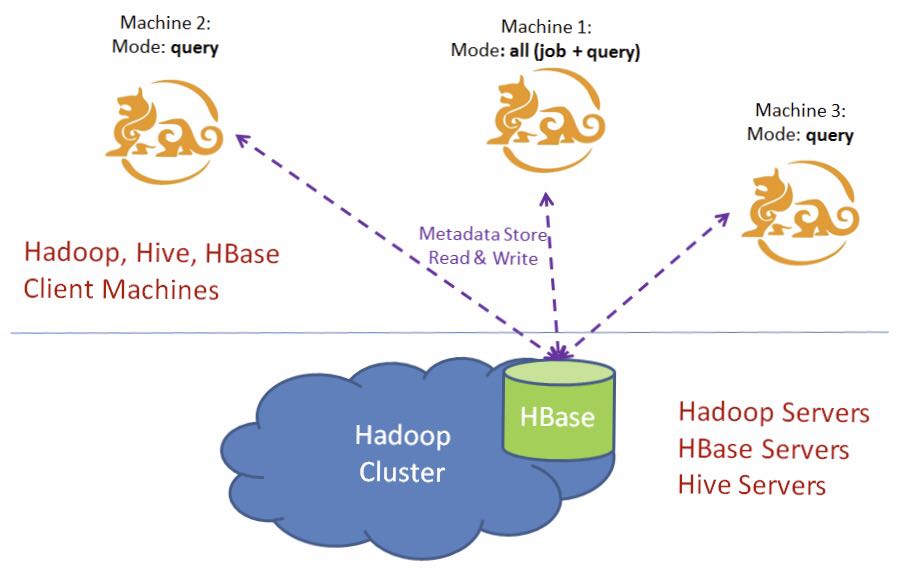
Kylin Node Configuration
If you need to cluster multiple Kylin nodes, make sure they use the same Hadoop cluster, HBase cluster. Then do the following steps in each node’s configuration file $KYLIN_HOME/conf/kylin.properties:
- Configure the same
kylin.metadata.urlvalue to configure all Kylin nodes to use the same HBase metastore. - Configure the Kylin node list
kylin.server.cluster-servers, including all nodes (the current node is also included). When the event changes, the node receiving the change needs to notify all other nodes (the current node is also included). - Configure the running mode
kylin.server.modeof the Kylin node. Optional values includeall,job,query. The default value is all.
The job mode means that the service is only used for job scheduling, not for queries; the query pattern means that the service is only used for queries, not for scheduling jobs; the all pattern represents the service for both job scheduling and queries.
Note: By default, only one instance can be used for the job scheduling (ie.,
kylin.server.modeis set toallorjob).
Enable Job Engine HA
Since v2.0, Kylin supports multiple job engines running together, which is more extensible, available and reliable than the default job scheduler.
To enable the distributed job scheduler, you need to set or update the configs in the kylin.properties:
kylin.job.scheduler.default=2
kylin.job.lock=org.apache.kylin.storage.hbase.util.ZookeeperJobLock
Please add all job servers and query servers to the kylin.server.cluster-servers.
Installing a load balancer
To send query requests to a cluster instead of a single node, you can deploy a load balancer such as Nginx, F5 or cloudlb, etc., so that the client and load balancer communication instead communicate with a specific Kylin instance.
Read and write separation deployment
For better stability and optimal performance, it is recommended to perform a read-write separation deployment, deploying Kylin on two clusters as follows:
- A Hadoop cluster used to Cube build, which can be a large cluster shared with other applications;
- An HBase cluster used to SQL query. Usually this cluster is configured for Kylin. The number of nodes does not need to be as many as Hadoop clusters. HBase configuration can be optimized for Kylin Cube read-only features.
This deployment strategy is the best deployment solution for the production environment. For how to perform read-write separation deployment, please refer to Deploy Apache Kylin with Standalone HBase Cluster .
